Why You Should Learn Data Visualisation
Most businesses have large amounts of data at its disposal regardless of the industry it operates in. However, even if a researcher gathers tons of useful information, it serves little purpose if clients or viewers are unable to understand it.
Translating research or business data is often difficult without visual representations. This is why the practice of data visualisation has become essential in turning data to effective, actionable information.
What is Data Visualisation?
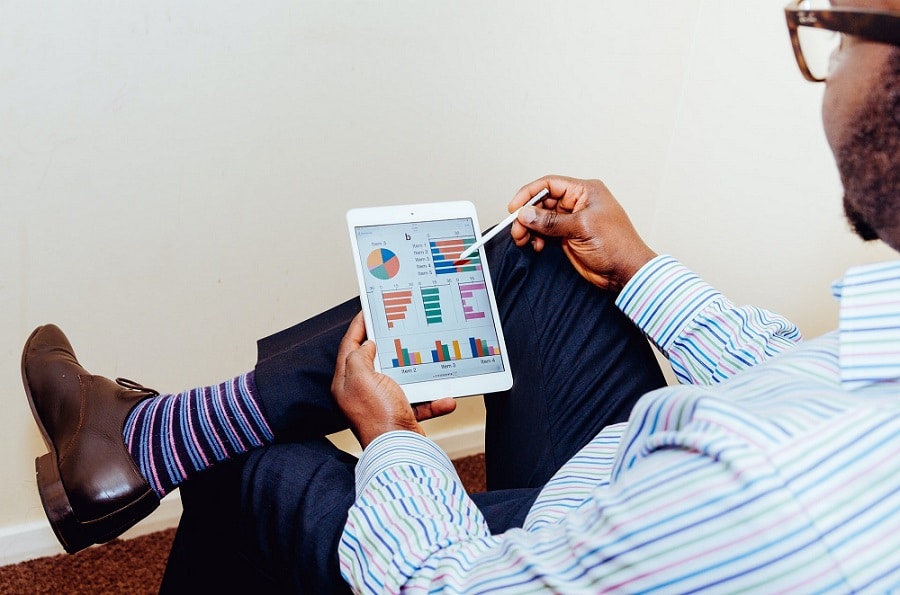
As the saying goes – “A picture is worth a thousand words.” Data visualisation refers to the process of translating and presenting data through the use of visuals, both static and interactive.
This visual format facilitates the process of understanding the data and communicates complex data relationships. It also helps in identifying outliers in the data set.
Why Learning Data Visualisation is Important
As data grows exponentially, there has never been a better time to become a data analyst. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics predicted that the demand for data professionals will grow about 28 per cent through 2026.
With the large disparity between the supply and demand of data professionals, this leads to an increase in salary as well. According to LinkedIn, the average annual starting salary for a data analyst in the United States was reported to be $90,000.
Data visualisation is a powerful tool for managing and breaking down the large volumes of information generated. Deriving meaningful and usable insights from the floods of big data is challenging enough, let alone identifying patterns and trends.
Therefore, data visualisation is necessary for today’s data analysts and other users – it makes it easier for researchers to explain their findings and allow readers to better comprehend data trends.
On top of that, the human brain is naturally wired to interpret visuals faster and more efficiently as compared to rows of data. It also has a tendency to find patterns in the things people see. Data visualisation leverages this and conveys concepts in a manner that is easy, fast, and universal.
So, if one is keen on acquiring data visualisation skills, it can be accomplished through participating in data analytics courses, conducted by organisations such as Vertical Institute. Fret not, these bootcamps are suitable for beginners who have no prior knowledge about data visualisation.
Benefits of Using Data Visualisation
Data visualisation offers a multitude of benefits that span across various industries. Here are some of the key benefits of visualising data.
1 – Increase the speed of decision-making processes
By presenting data through graphical representations, businesses are able to view large amounts of data in a clear and cohesive way. Instead of sifting through information in the form of spreadsheets, businesses can quickly draw conclusions from the visualised data and make decisions in a more timely manner.
Speeding up the decision-making process is crucial for enterprises as they can then take opportune action on trends or avert unexpected losses.
2 – Identify relationships and patterns
Data visualisation enables businesses to recognise relationships between the data, attributing greater meaning to it.
Businesses will also be able to spot and explore patterns, focusing on specific areas that require attention in the data. By identifying the significance of those areas, it can help to drive their business forward.
3 – Pinpoint emerging trends
Visualising data allows users to discover trends both in their business and the market they operate in. By staying on top of trends, it will help businesses to gain an edge over their competitors.
Moreover, data visualisation makes it easier to spot outliers that are affecting product quality or customer churn. Thus, businesses will be able to address issues before they arise or become bigger.
4 – Communicate the story easily to others
After deriving insights from the data, the following step is to communicate the information to others. Using visual aids such as charts or graphs helps to get the message across quickly and in an engaging manner.
Data visualisation also promotes communication and collaboration as multiple viewers are able to observe, appreciate and discuss the insights. This increases the opportunity of sharing information efficiently with as many people as possible.
Types of Data Visualisation
One must note that the effectiveness of data visualisation is also dependent on the way it is executed. There are various types of visualisation techniques along with their intended outcomes, thus it is important to match the data to the right technique.
1 – Area charts
Area charts are a variation of the line chart. However, what sets them apart is that in an area chart, the space between the x-axis and the plotted line is coloured in.
The area chart is useful for highlighting the difference between multiple variables, or to measure overall volumes. Also, an area chart should not have more than four or five datasets simultaneously, as it will cause the chart to become cluttered.
2 – Bar charts
Bar charts are one of the most common types of data visualisation. Otherwise known as column charts, these are simple yet highly effective ways of comparing data along two axes.
The height or width of the bars are placed in direct proportion to the values that they represent. To determine between using a bar or column chart, first observe the data. If the qualitative data uses long, descriptive names, then a horizontal/bar chart would be the most suitable.
3 – Line graphs
Line graphs are useful for showcasing changes in data over time and it can consist of one or several lines. In the event where there are multiple lines, each one represents a category. Each category is then given a colour and the description is given in the legend.
To avoid confusion, line graphs should contain no more than five lines and it is important to ensure that the colours of each line are differentiable.
4 – Pie charts
Pie charts are another common type of data visualisation. Each pie chart represents one variable, split into different proportions.
Ideally, pie charts should not have more than five parts. Adding too many categories will result in some of the wedges becoming too thin, making it unable to effectively present the data. Additionally, each wedge should be represented by contrasting colours to make it easy to discern the difference.
5 – Scatterplots
Scatterplots are often used to understand the correlation between two variables. Outliers, which are the data points located outside of the expected range, should be noted and analysed when observing the data.
Scatterplots are best for hypothesis creation rather than drawing firm conclusions due to the possibility that other factors are affecting the data as well. Also, one should avoid plotting too many data points as this will cause the scatterplot to become difficult to read.
Conclusion
In a world that is data-driven, data visualisation is an essential skill in translating data into actionable and understandable information. Tableau is also one of the leading data visualisation tools that is a must to learn.