Important Things to Know About Calibration Software Solutions
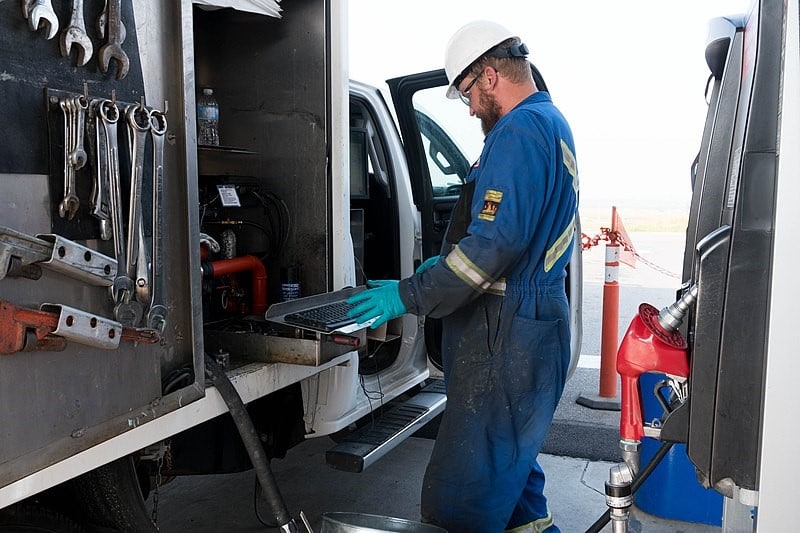
Most manufacturing industries require the use of measurement devices like scales, gauges, thermometers, infrared meters, etc. to make sure that every manufacturing section is working optimally. In the past, these industries relied on handheld devices to maintain accurate and consistent calibration.
However, these days, instead of relying on manual calibration (which is not practical in respect to the size of most industries), most corporations are making use of calibration software solutions to ensure proper control and performance.
These software solutions are still new to many; therefore, we have written this article to explain to you what calibration software is as well as important things you need to know about this solution.
Let’s begin…
What a Calibration Software Is
Calibration software solutions are made up of a measurement equipment and devices database that is utilized in a company to track calibrations for accuracy purposes. This software allows the user to manage device data, devices, as well as calibration efforts with the aid of a single central interface.
With the aid of such a solution, your adjustment events can be performed on time and accurately. This will in turn enhance the quality results and also reduce errors while creating a standard for asset management.
Equipment managers and technicians can use such software for maintenance schedules which will help them free up time that can be dedicated to other vital tasks.
Thanks to the ability of this solution to keep accurate historical records, organization within the industry is made easier and compliant with the company’s quality standards.
Areas Calibration Software Solutions Help
The overall purpose of using this solution is to enhance productivity and it does this by helping out in the main areas of tasks/stages that companies perform.
Let’s quickly take a look at these areas…
1. Planning and Decision-Making
To help in this area, all the measurement devices and plant instruments must first be listed and after that classified into two categories of devices which are “non-critical” and “critical”. After you have that set up, then you need to recognize the range of standardization as well as tolerance requirement.
Each instrument’s calibration interval must then be decided upon. This is followed by creating and approving the SOP (Standard Operating Procedures) for each instrument. Click here to learn more about SOP. Then the perfect method of standardization is selected and the execution tools for each method are chosen.
After this, the identification of each device’s standardization status throughout the manufacturing plant is done.
2. Organization
After the planning and decision-making stage, you then move to the organization stage. In this stage, you have to train the calibration staff which is made up of the service engineers, maintenance technicians, process and quality managers, and engineers. They are to be trained on how to comply with the SOPs that were approved in the previous stage.
The availability and assignment of resources to the appropriate quarter are vital to ensure that this area is executed efficiently.
3. Execution
Speaking of “executed”, the next area is the execution phase. This involves the supervision of the standardization tasks that have been assigned. Staff that has been assigned the activities must be monitored to ensure their compliance to the instructions before they carry out their duties.
They are also required to follow the safety procedures that have been put in place. Proper supervision will ensure that the standardization is executed as planned. Yet, they must be flexible enough to adhere to new instructions that may be given after the calibration.
The results will have to be electronically signed or the generated records will have to be approved. Both the results and records will have to be documented and stored.
The results will then present an opportunity for further analysis which will then allow you to decide if there is a need for corrective actions. The calibration effectiveness should be reviewed while the intervals should be checked. This is important as you might have to change the intervals according to the standardization history.
4. Documentation
This is a vital area of management that must not be neglected. You can understand the importance of this area from the fact that auditors and regulatory agencies require that proper documentation of procedures be maintained. Without proper documentation, all the activities performed cannot be regarded as calibration. Visit https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3122044/# to find out why documentation is a good manufacturing practice.
With this solution, the time spent on paperwork documentation is eliminated allowing the instrument engineer to document the results and records of thousands of devices within a short period.
5. Analysis
With the aid of this software, analysis is more accurate, easier, and faster. Identification of historical trends is also easy to accomplish. As a result, the cost is reduced while calibration intervals are optimized by reducing or increasing standardization frequency as the case may be.
Conclusion
With a good calibration software solution, you can improve the overall efficiency of your manufacturing plant and cut down on unnecessary waste and loss.