12 Open Source Alternatives to ChatGPT and Bard: Empowering the Community with AI Creativity
Artificial intelligence (AI) has become an essential part of our lives, transforming industries and revolutionizing the way we interact with technology. Among the many applications of AI, language models have gained significant attention, especially in the domain of natural language processing (NLP). ChatGPT and Bard, developed by OpenAI, are powerful language models that have been used for a wide range of tasks, including chatbots, creative writing, and content generation.
However, despite their capabilities, ChatGPT and Bard are proprietary software, and their access and usage may be limited due to licensing and usage restrictions. This has sparked interest in the open-source community to develop alternative solutions that are free, transparent, and community-driven. In this article, we will explore some of the open-source alternatives to ChatGPT and Bard that are available, and how they empower the community with AI creativity.
Chatbots and AI-powered assistants have become increasingly popular in recent years, offering a range of benefits to businesses and individuals alike. While proprietary solutions like ChatGPT and Bard are well-known, there are also several open source alternatives available. In this article, we will explore some of the top open source alternatives to ChatGPT and Bard, including Alpaca, LLaMA, Vicuna, OpenChatKit, GPT4ALL, Raven RWKV, OPT, and Flan-T5-XXL.
1. Alpaca
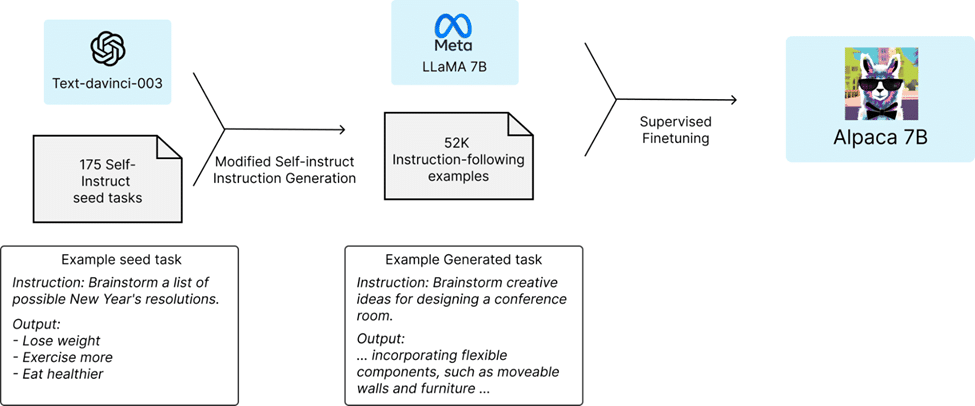
Alpaca is an open source chatbot development framework that focuses on providing an easy-to-use and flexible solution for building conversational AI applications. It offers a range of tools and features for building chatbots, including natural language processing, dialogue management, and machine learning. Alpaca is written in Python and can be easily integrated with other popular libraries and platforms.
Stanford Alpaca claims that it can compete with ChatGPT and anyone can reproduce it in less than 600$. One of the key benefits of using Alpaca is its focus on customization. It allows developers to easily define custom intents, entities, and responses, making it highly adaptable to different use cases. Alpaca also offers a range of pre-built integrations with popular chat platforms, such as Facebook Messenger and Slack.
Resources:
- Blog: Stanford CRFM
- GitHub: tatsu-lab/stanford_alpaca
- Demo: Alpaca-LoRA (The official demo was drop and this is a recreation of Alpaca model)
2. LLaMA
LLaMA (Language Learning and Modeling Agent) is an open source chatbot development framework developed by Carnegie Mellon University. It is designed specifically for building chatbots that can learn and adapt to user inputs over time. LLaMA uses a combination of deep learning and reinforcement learning techniques to continuously improve its responses based on user interactions.
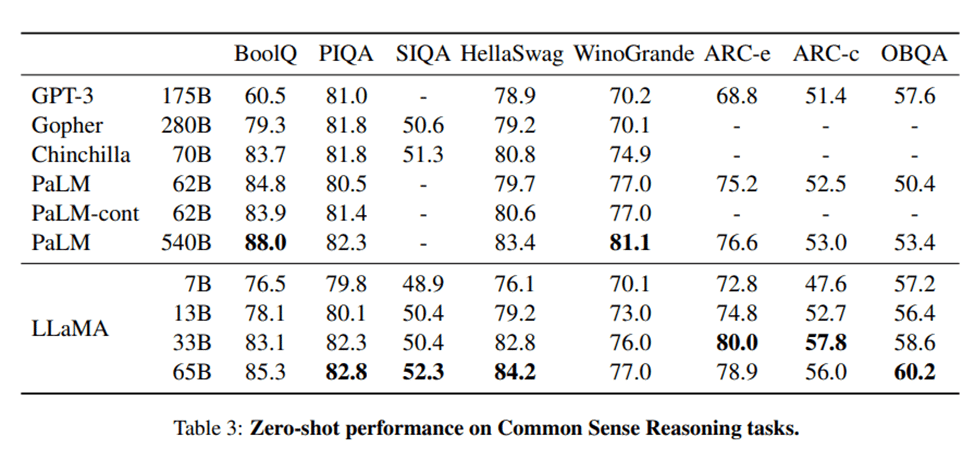
One of the key benefits of using LLaMA is its focus on machine learning and adaptability. It offers a range of pre-built models for different types of conversations, such as small talk, news, and customer support, and can be easily trained on custom datasets. LLaMA also offers a user-friendly interface for managing and monitoring chatbot conversations.
Resources:
- Research Paper: LLaMA: Open and Efficient Foundation Language Models (arxiv.org)
- GitHub: facebookresearch/llama
- Demo: Baize Lora 7B
3. Vicuna
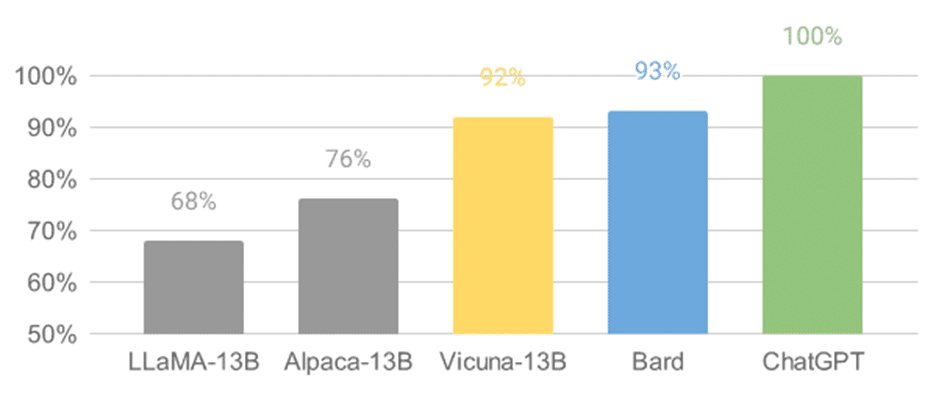
Vicuna is an open source chatbot development platform developed by IBM. It offers a range of tools and features for building AI-powered assistants, including natural language processing, dialogue management, and machine learning. Vicuna is built on top of the popular Watson Assistant platform and offers a range of pre-built models and integrations.
One of the key benefits of using Vicuna is its scalability. It is designed to handle large volumes of data and can be easily integrated with other IBM services, such as Watson Discovery for knowledge extraction and Watson Studio for custom model training. Vicuna also offers a user-friendly interface for designing and managing chatbot conversations.
Resources:
- Blog post: Vicuna: An Open-Source Chatbot Impressing GPT-4 with 90%* ChatGPT Quality
- GitHub: lm-sys/FastChat
- Demo: FastChat (lmsys.org)
4. OpenChatKit
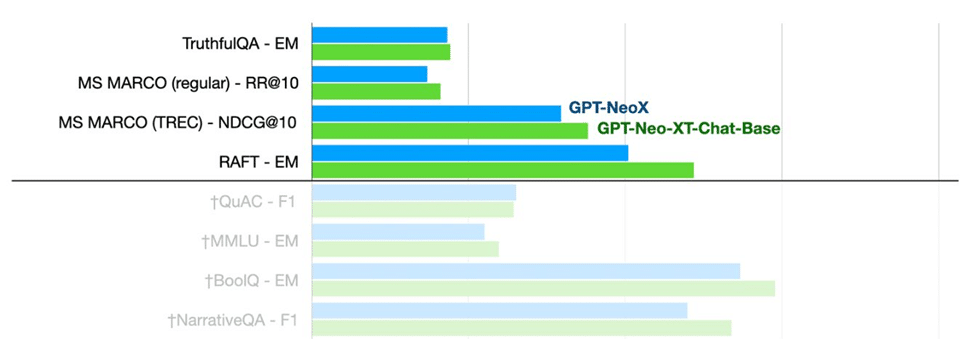
OpenChatKit is an open source chatbot development framework that focuses on providing a lightweight and customizable solution for building chatbots. It offers a range of tools and features for building conversational AI applications, including natural language processing, dialogue management, and machine learning. OpenChatKit is written in Python and can be easily integrated with other popular libraries and platforms.
One of the key benefits of using OpenChatKit is its flexibility. It allows developers to easily define custom intents, entities, and responses, making it highly adaptable to different use cases. OpenChatKit also offers a range of pre-built integrations with popular chat platforms, such as Facebook Messenger and Slack.
Resources:
- Blog Post: Announcing OpenChatKit — TOGETHER
- GitHub: togethercomputer/OpenChatKit
- Demo: OpenChatKit
- Model card: togethercomputer/GPT-NeoXT-Chat-Base-20B
5. GPT4ALL
GPT4ALL is an open source chatbot development platform that focuses on leveraging the power of the GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) model for generating human-like responses. It offers a range of tools and features for building chatbots, including fine-tuning of the GPT model, natural language processing, and dialogue management. GPT4ALL is written in Python and can be easily integrated with other popular libraries and platforms.
One of the key benefits of using GPT4ALL is its ability to generate high-quality responses that are similar to human responses. The GPT model is trained on a large corpus of text data, making it highly capable of generating contextually relevant and coherent responses. GPT4ALL also offers flexibility in fine-tuning the model for specific use cases, making it adaptable to various industries, such as customer service, sales, and support.
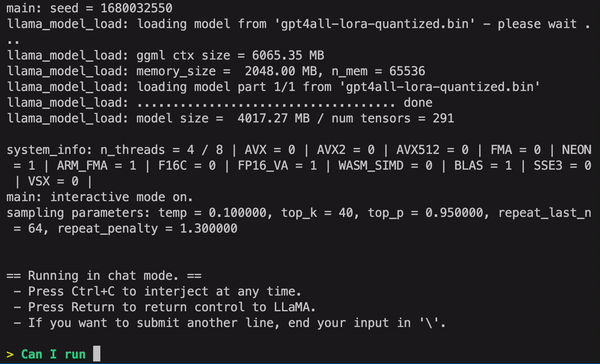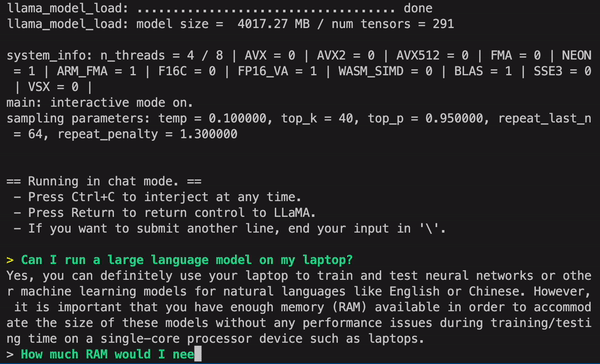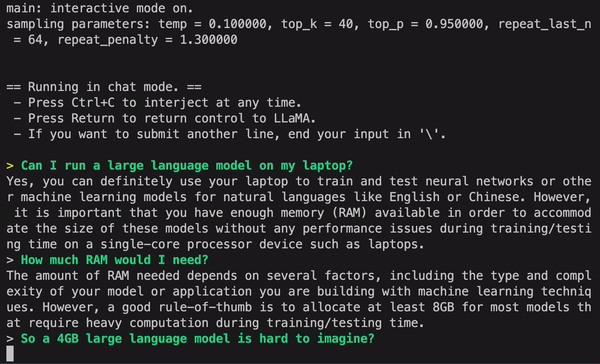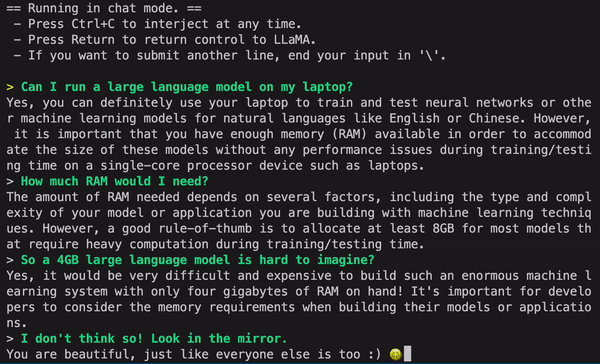
- Resources:
- Technical Report: GPT4All
- GitHub: nomic-ai/gpt4al
- Demo: GPT4All (non-official)
- Model card: nomic-ai/gpt4all-lora · Hugging Face
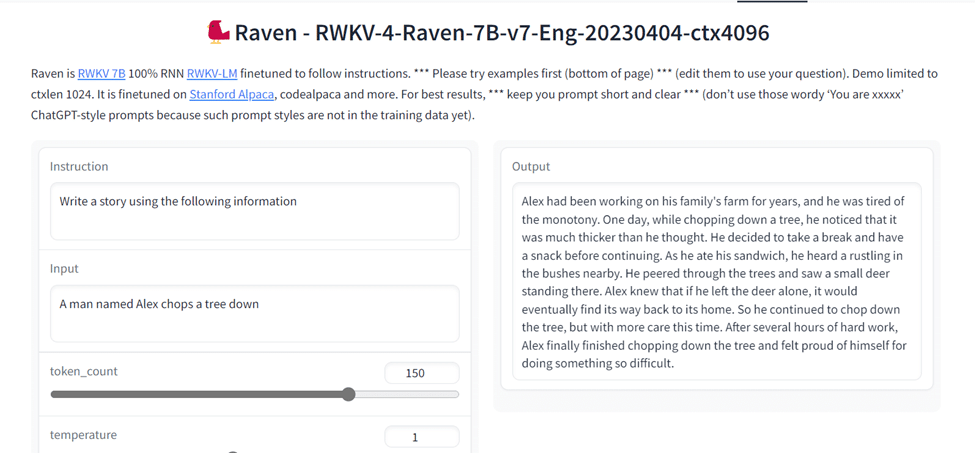
6. Raven RWKV
Raven RWKV is an open source chatbot development framework that is focused on providing a knowledge-driven approach to building chatbots. It offers a range of tools and features for building chatbots, including knowledge extraction, natural language processing, dialogue management, and machine learning. Raven RWKV is written in Python and can be easily integrated with other popular libraries and platforms.
One of the key benefits of using Raven RWKV is its emphasis on knowledge extraction. It allows developers to easily extract knowledge from different sources, such as documents, websites, and databases, and use that knowledge to generate informed responses. Raven RWKV also offers a user-friendly interface for managing and updating the knowledge base, making it easy to keep the chatbot up-to-date with the latest information.
Resources:
- GitHub: BlinkDL/ChatRWKV
- Demo: Raven RWKV 7B
- Model card: BlinkDL/rwkv-4-raven
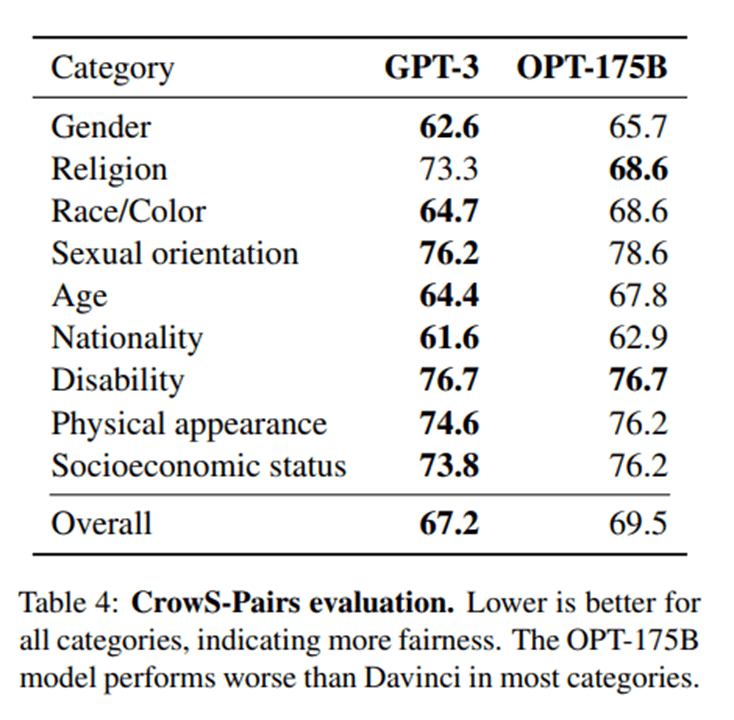
7. OPT
OPT (Open Parameterized Transformer) is an open source chatbot development framework that focuses on providing a highly customizable and extensible solution for building chatbots. It offers a range of tools and features for building conversational AI applications, including natural language processing, dialogue management, and machine learning. OPT is written in Python and can be easily integrated with other popular libraries and platforms.
One of the key benefits of using OPT is its flexibility in parameterizing and customizing the transformer model. It allows developers to easily define custom parameters, such as context window size, attention mechanisms, and model architecture, making it highly adaptable to different use cases. OPT also offers a range of pre-built integrations with popular chat platforms, such as Facebook Messenger and Slack.
Resources:
- Research Paper: OPT: Open Pre-trained Transformer Language Models (arxiv.org)
- GitHub: facebookresearch/metaseq
- Demo: A Watermark for LLMs
- Model card: facebook/opt-1.3b
8. Flan-T5-XXL
Flan-T5-XXL is an open source chatbot development framework that is built on top of the T5 (Text-to-Text Transfer Transformer) model, which is a state-of-the-art transformer-based language model. Flan-T5-XXL offers a range of tools and features for building chatbots, including fine-tuning of the T5 model, natural language processing, dialogue management, and machine learning. It is written in Python and can be easily integrated with other popular libraries and platforms.
One of the key benefits of using Flan-T5-XXL is its capability to generate highly contextual and coherent responses. The T5 model is trained on a large corpus of text data, making it highly capable of understanding and generating human-like responses. Flan-T5-XXL also offers a range of pre-built datasets and models for different types of conversations, making it easy to get started with building chatbots for various domains.
Resources:
- Research Paper: Scaling Instruction-Fine Tuned Language Models
- GitHub: google-research/t5x
- Demo: Chat Llm Streaming
- Model card: google/flan-t5-xxl
9. GPT-2 and GPT-3 by OpenAI
While ChatGPT and Bard are proprietary software, OpenAI has released the GPT-2 and GPT-3 models as open source. GPT-2, released in 2019, is a large-scale language model with 1.5 billion parameters, capable of generating coherent and contextually relevant text. GPT-3, released in 2020, is even more powerful, with a whopping 175 billion parameters, making it one of the most advanced language models to date.
Both GPT-2 and GPT-3 have been used in various creative applications, including chatbots, text generation, and storytelling. OpenAI has provided extensive documentation, tutorials, and code examples to facilitate the usage of these models, making them accessible to the open-source community for research and development purposes.
10. Hugging Face Transformers
Hugging Face is a popular open-source platform for NLP, and it has developed the Transformers library, which provides a wide range of pre-trained models, including variants of the GPT model. The Transformers library is written in Python and offers a user-friendly API that makes it easy to fine-tune the models for specific tasks or generate text creatively.
The Transformers library has gained widespread popularity in the NLP community due to its versatility, ease of use, and extensive documentation. It has been used in a wide range of applications, from chatbots and content generation to machine translation and sentiment analysis. Hugging Face also provides pre-trained models in different languages, allowing developers to build multilingual applications using the same framework.
11. GPT-Neo by EleutherAI
GPT-Neo is an open-source project by EleutherAI, a community-driven research organization focused on developing advanced AI models. GPT-Neo aims to provide an alternative to proprietary language models like ChatGPT and Bard, by providing open-source implementations of large-scale language models.
GPT-Neo comes in different sizes, ranging from “tiny” models with 1.3 billion parameters to “mega” models with 19 billion parameters, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. The project is hosted on GitHub and provides extensive documentation and code examples, making it easy for developers to get started with GPT-Neo.
12. DialoGPT by Microsoft
DialoGPT is an open-source language model developed by Microsoft Research, specifically designed for dialogues and conversations. DialoGPT is trained using a dialogue dataset, which makes it well-suited for chatbot applications and interactive conversations.
Microsoft has released the DialoGPT model on GitHub, along with code examples and tutorials for fine-tuning and using the model. DialoGPT has many potential applications in various fields such as customer service, education, and entertainment. It can be used to build conversational agents, chatbots, and virtual assistants that can interact with users in a natural and engaging way.
Overall, DialoGPT is an impressive language model that has the potential to revolutionize the way we interact with machines and technology. Its ability to generate coherent and relevant responses to natural language input is a significant step forward in the field of natural language processing, and we can expect to see many exciting developments in this area in the coming years.
Conclusion
Open source alternatives to ChatGPT and Bard offer a range of benefits for developers and businesses, including customization, adaptability, scalability, and flexibility. Overall, these open source alternatives offer a viable option for developers and researchers who want to work with natural language processing and generation. They are free to use, transparent, and can be customized to fit specific use cases and applications.


























