SQL is what’s next for Hadoop
Today all the companies are trying to let users run SQL queries from inside Hadoop as it is open-source software framework. Companies are using Hive and HiveQL languages in Hadoop implementation but Hive is mainly depends on MapReduce. Business intelligence and database products like EMC Greenplum, HP Vertica, IBM Netezza, ParAccel, Microsoft SQL Server and Teradata/Aster Data are useful to access to Hadoop data.
Here are the details of companies are offering some innovative Hadoop and analytics tools. The applications, frameworks and engines that let users query Hadoop data from inside Hadoop, sometimes by re-architecting the underlying compute and data infrastructures.
Data warehouses and BI Tools:
Apache Drill: Apache Drill is an open-source software framework that supports data-intensive distributed applications for interactive analysis of large-scale datasets. Drill is the open source version of Google’s Dremel system which is available as an infrastructure service called Google BigQuery. One explicitly stated design goal is that Drill is able to scale to 10,000 servers or more and to be able to process petabyes of data and trillions of records in seconds. Currently, Drill is incubating at Apache.
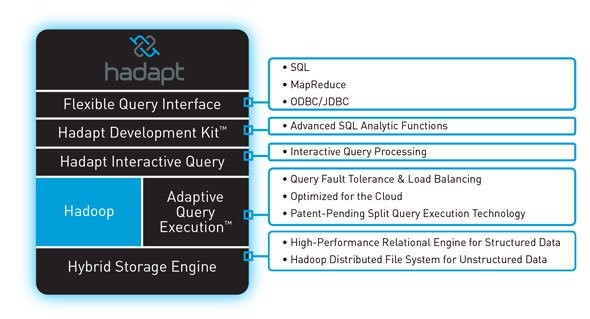
Hadapt: Hadapt offers an adaptive analytical platform for performing complex analytics on structured and unstructured data, all in one cloud-optimized system. Its unique architecture includes tools for advanced SQL functions and a split-execution engine for MapReduce and relational tasks, and both HDFS and relational storage.
Platfora : Platfora is a fully featured, enterprise-class business intelligence application. Built on HTML5, it is accessible anywhere and there are no per-user licensing limits. Collaboration and sharing is built in. With Platfora, analysts can drill into detail or dimensions only available in raw data without the IT friction and complexity of traditional solutions.
Platfora transforms Apache Hadoop from batch engine into a subsecond-interactive, exploratory business intelligence and analytics platform designed for business analysts. This has never been done before, and getting there involves far more than putting a pretty user interface on top of Hadoop.
Qubole: The Qubole Data Service (QDS) is a Software-as-a-Service analytics platform running on leading cloud offerings like Amazon Web Services (AWS). Targeted towards data analysts, data scientists and ETL engineers – it can help users to get started analyzing data in a matter of minutes. QDS is built on top of Apache Hadoop, Hive, Pig, Oozie and Sqoop. Users can explore cloud data sets, model them and query them using our best-in-class cloud Hadoop offering. They can import data, build sophisticated data pipelines and export data sets to various sources – all from the browser. Expert users can take advantage of our REST APIs to run workloads against our auto-scaling Hadoop clusters from within their applications.
Citus Data: CitusDB is a distributed database that lets you run SQL queries over very large data sets. Designed for analytical queries, CitusDB enables real-time responsiveness. CitusDB colocates database instances on Hadoop nodes, and removes any network bottlenecks. Lets you instantly run SQL queries on Hadoop clusters without having to load any data into the database.
Cloudera Impala: Cloudera Impala provides fast, interactive SQL queries directly on your Apache Hadoop data stored in HDFS or HBase. In addition to using the same unified storage platform, Impala also uses the same metadata, SQL syntax (Hive SQL), ODBC driver, and user interface (Hue Beeswax) as Apache Hive. This provides a familiar and unified platform for batch-oriented or real-time queries. Cloudera Impala is an addition to tools available for querying big data. Hive and other frameworks built on MapReduce are best suited for long running batch jobs, such as those involving batch processing of Extract, Transform, and Load (ETL) type jobs.
Karmasphere: Karmasphere is one of the first startups to build an analytic application atop Hadoop, and in its 2.0 release last year the company added support for SQL queries of data in HDFS. Like Hive, Karmasphere still relies on MapReduce to process queries, which means it’s inherently slower than newer approaches. However, unlike Hive, Karmasphere allows for parallel queries to run at the same time and includes a visual interface for writing queries and filtering results.
Lingual: Lingual executes ANSI SQL queries as Cascading applications on Apache Hadoop clusters. Lingual was created in collaboration by the developers of Cascading and Optiq, and relies on the robustness of both. Cascading is the de facto Java API for creating complex data processing workloads and the engine underneath Scalding, Cascalog, and others.
Phoenix: Phoenix is a SQL layer over HBase, delivered as a client-embedded JDBC driver, powering the HBase use cases at Salesforce.com. Phoenix targets low-latency queries (milliseconds), as opposed to batch operation via map/reduce. The Phoenix query engine transforms your SQL query into one or more HBase scans, and orchestrates their execution to produce standard JDBC result sets. Direct use of the HBase API, along with coprocessors and custom filters, results in performance on the order of milliseconds for small queries, or seconds for tens of millions of rows.
Shark: Shark is a large-scale data warehouse system for Spark designed to be compatible with Apache Hive. It can answer Hive QL queries up to 100 times faster than Hive without modification to the existing data nor queries. Shark supports Hive’s query language, metastore, serialization formats, and user-defined functions.
Stinger Initiative: The Stinger Initiative is a Hortonworks-led effort to make Hive faster- up too 100x -and more functional. Stinger adds more SQL analytics capabilities to Hive, but the most-important aspects are infrastructural: an optimized execution engine, a columnar file format and the ability to avoid MapReduce bottlenecks by running atop Tez.
Drawn to Scale: Drawn to Scale is offering the solution called Spire and is the-the first SQL database for large, user-facing applications built on Hadoop. Spire is built to power large-scale websites, mobile apps, and machine-to-machine data. Unlike any other Hadoop and SQL solution, Spire scales to tens of thousands of reads and writes per second, with full ANSI SQL and intuitive management tools. Spire is architecturally very similar to Google F1 and makes it simple to build applications for the Big Data Era.
Splice Machine: Database startup Splice Machine is offering Splice SQL Engine. The Splice SQL Engine delivers a massively scalable database without the compromises of NoSQL or traditional relational databases. Companies can use it to access their Big Data without having to rewrite existing SQL-based applications or Business Intelligence (BI) tools. Built on the proven Hadoop stack, the Splice SQL Engine extends HBase to provide robust SQL support, secondary indexes, join optimizations and transactional integrity.
























