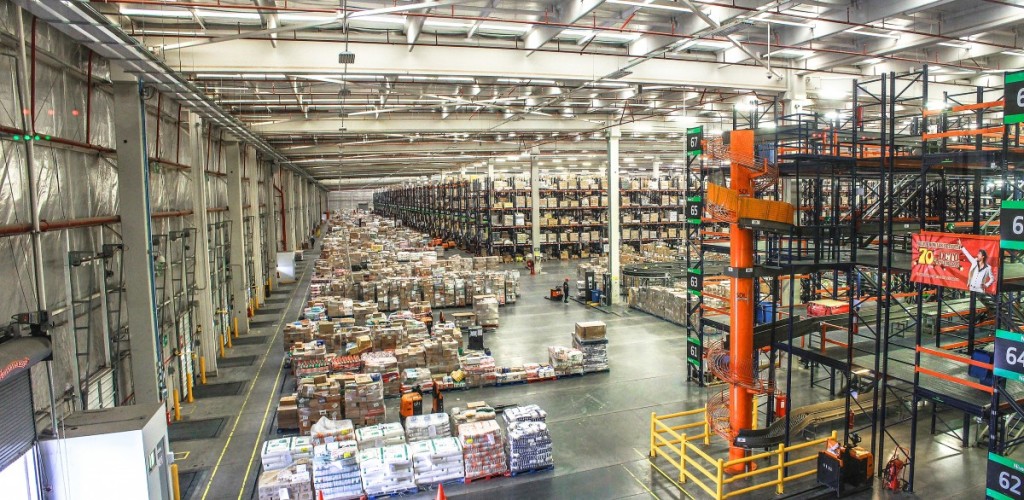
Why Do Logistics Need Data Collection?
Benefits of Data Collection in Logistics
Logistics is a set of organizational and management processes aimed at streamlining the movement of goods and services from supplier to consumer. In simple words, the main purpose of logistics is to find the most optimal and cost-effective ways of delivering products to the end consumer.
Logistics became an independent economic area in 1980 and has rapidly grown with every passing year. And nowadays, no medium or large enterprise can operate without the services of a logistics manager or a third-party logistic company.
This rapid progress in logistics requires specialists to work with huge volumes of data: databases of transport shipments for different regions and even countries, databases of suppliers, customers, etc. That is why automatic data collection and optimization are becoming increasingly important in modern logistics.
Types of Logistics
In order to understand the importance of data collection and its impact on the efficiency of logistics, it is essential to grasp it from the inside. Let’s first focus on the main types of logistics and their applications:
- Inbound logistics is the type that is invisible to the consumer but vital for the end product. Inbound logistics is the delivery of raw materials or components to the plant that manufactures the product itself. The complexity of inbound logistics is determined by the scale and scope of a company’s business. As an example, to arrange supplies for the publishing industry, the logistician will coordinate the purchase and delivery of ink and paper. But if you have a confectionery shop and you need perishable imported goods, the logistician will have to coordinate the purchase, storage, and delivery according to many sanitary and technological standards.
- The outbound type of logistics is the shipping of the final product to the consumer. The main purpose of this type is to deliver the product in the shortest time and with minimal expenses. Outbound logistics plays an important role in the company’s image. That’s why marketers try to highlight the company’s benefits in logistics, for example, same-day delivery. Correct distribution and optimization of delivery channels and customer bases play a decisive role in the success of outbound logistics.
- Reverse logistics is the process of shipping the final product from the consumer to the producer. To put it simply, it’s a return. In case the product is substandard or unsuitable for the customer, the consumer requests an exchange or a refund. In this case, the logistics company delivers the goods to the starting point. It is important to organize the reverse logistic process properly. Otherwise, you may face high costs and a decrease in customer confidence.
- Third-party logistics (3PL) implies the transfer of all logistics operations to a third-party company. If a business does not have sufficient resources to assemble its own fleet and arrange logistics chains, it uses the services of a logistics company. Such firms provide a variety of services: from point-to-point delivery to insurance and storage.
Basic Steps of the Logistics Cycle
Effective logistics is well-coordinated procurement and transportation of goods and materials. The entire logistics process is separated into several stages and follows a certain cycle. Depending on the nature of the company’s business, this cycle may vary, but typically it contains four main stages:
- Customer service
- Forecasting and procurement
- Receiving and storage
- Transportation & delivery
Let’s talk more in-depth about each step to determine the volume of data processed by the logistician and the importance of data collection automatization.
Customer Service
It’s essential to keep in mind that logisticians work to fulfill the needs of customers first and foremost. All logistics processes have to be carried out in such a way that the customer is satisfied.
Proper storage of goods, on-time delivery and courteous couriers, well-tuned operators, and a willingness to solve customer problems — all of this makes for a positive customer experience.
Well-organized logistics greatly influence the customer’s opinion of the company. To keep the customer satisfied, services need to be constantly improved. To maximize results, it is necessary to improve logistics systems by optimizing the movement of goods and information. Any deficiencies here should be resolved through a strategic audit and system redesign.
Forecasting and Procurement
Forecasting is a crucial step in the logistics cycle. Clear planning and in-depth analysis insure you against unfavorable actions and decisions.
At the forecasting stage, it is necessary to determine what goods are worth procuring and in what quantity, what is currently in demand among customers, which ways are easiest to deliver goods, etc.
For accurate and profitable forecasts, it is necessary to collect large amounts of data and analyze them quickly. For such complex operations, a logistics company needs to have the latest software and hardware.
Receiving and Storage
During the receiving and storage phase, the logistics company receives the goods, checks them for defects, and selects the proper storage standards.
After receiving the goods, the logistics company determines which warehouse to send them to. For example, perishables and medicines need to be stored in temperature-controlled warehouses.
At the warehouse, the goods are labeled, entered into the database, and prepared for unloading and redistribution or sale.
Transportation & Delivery
Transportation and delivery is the final stage of the logistics cycle, except for returns, but it is often included here as well. Transportation is arranged in accordance with the commercial contract and can be requested by the seller as well as by the purchaser.
At this stage, it is important to optimize the load of the carrier so that all goods are delivered on time to every recipient, regardless of the location. It is also important to follow the packing and delivery regulations depending on the category of goods.
Why Data Collection Is Important in Logistics
So how can data collection automatization help you? In fact, automation software can solve various issues at each stage of the logistics cycle. There is a large variety of software that, for example, only automates the work of the warehouse or optimizes the collection of information about orders and customers. There is also multi-component software that solves issues at every stage of the cycle. Before introducing such technology into your business, you should first decide what issues you need to solve.
Here are the most common areas in logistics where you can use automation software:
- Transportation. In this area, the software is able to fully track the fleet, from the number of miles driven to the condition of the vehicle. The software also monitors road conditions and creates optimal routes. Excessive fuel consumption can also be solved by the optimization of the process of transporting goods.
- Warehousing. At the stage of product warehousing, the logistician has to work with the largest amount of information. The software is able to control the process of goods receipt, storage, and shipment. It is also possible to create a large-scale 3D map of the warehouse, synchronized with the barcodes on the goods. Thus the storage will be optimized to the maximum;
- Reporting and invoicing. The source of unnecessary expenses is extremely difficult to identify. But automation software handles this issue perfectly. The program will track the cost of each item, shipping costs, storage, and even the cost of electricity in the warehouse. With that kind of data, no penny will slip past you;
- Customer service management. Working with the customer requires a lot of time and involves storing a lot of information. The software is able to store, analyze and synchronize all data about customers and services. The system will monitor the entire process from order to delivery.
Logistics software for data collection and optimization can solve many of your problems. IT companies specializing in logistics development are well aware of this industry and develop software to solve the most pressing logistics issues.
Conclusion
The main purpose of logistics is optimization. But the industry is growing, there are more and more goods and routes, and a person is no longer able to cope with the rising amount of information. Data collection automatization saves time and money, which is the key point in logistics.