Pivotal Brings In-Memory Analysis To Hadoop
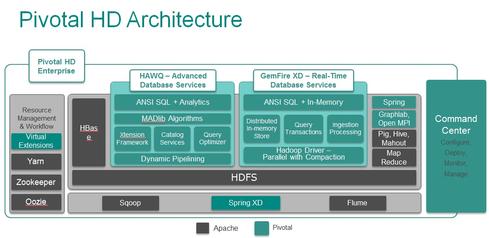
Pivotal HD 2.0 is the vendor’s first distribution based on Apache Hadoop 2.2, the latest release of the open source platform incorporating YARN system resource management controls. The release also integrates and supports Apache GraphLab, an open source framework for derivatives monitoring, recommendations, and graph analytics.
The big news, however, is the addition of GemFire XD, an in-memory database designed to execute algorithms and analytics on data in real time. Blending elements of Pivotal’s GemFire (in-memory object grid) and SQL Fire (in-memory database), GemFire XD puts a SQL-compliant, in-memory database on top of the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), from which it can read data or write data with ultra-low latency.
GemFire XD could be used by a mobile network provider, for example, to determine the identity, location, device, and network of an incoming call within an instant and then apply complex algorithms or in-memory analytics to determine how to route the call making the best use of available capacity. The database could also handle data-transformation tasks before writing the data to HDFS, circumventing the need for processing that might otherwise be required by way of ETL routines.
The Hadoop community is lately looking to Apache Spark as an open-source option for in-memory and stream processing capabilities, but Pivotal says commercial GemFire XD has many advantages over that technology.
“We’re excited about Spark and will support it, but it’s generally used for [data] ingest or caching,” said Michael Cucchi, Pivotal’s senior director of product marketing, in an interview with InformationWeek. “GemFire XD is an ANSI-compliant SQL database with high-availability features, and it can run over wide-area networks, so you can have an instance in Europe and another in North America with replication.” Read more
























